GitHub Integration #
Setting up the connection between GitHub and FASTEST is essential for automated analysis and testing. This comprehensive guide walks you through the three-step configuration process to fully integrate your repositories with the FASTEST platform.
Integration Overview #
The GitHub integration process consists of three main steps:
- Add Secret Key: Generate and configure a secure token for authentication
- Add Workflow Files: Install GitHub Actions workflows for automation
- Trigger the Workflow: Activate the integration through pull requests or code changes
Step 1: Add Secret Key #
The secret key enables secure communication between FASTEST and your GitHub repository.
Generate Token in FASTEST #
1. Access Configuration Tab
- Navigate to your FASTEST dashboard
- Click on the "Configure" tab or configuration section
- Select the repository you want to configure
2. Generate New Token
- Click the "Generate New Token" button
- FASTEST will create a unique authentication token for your repository
- Important: Copy this token immediately - it won't be shown again for security reasons
Configure GitHub Repository Secret #
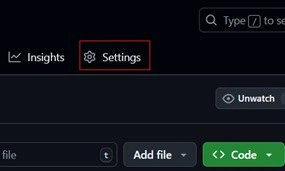
1. Navigate to Repository Settings
- Go to your GitHub repository
- Click on Settings tab (you need repository admin access)
- Navigate to Secrets and variables → Actions → Secrets
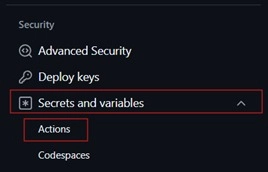
2. Add New Repository Secret
- Click "New repository secret" button
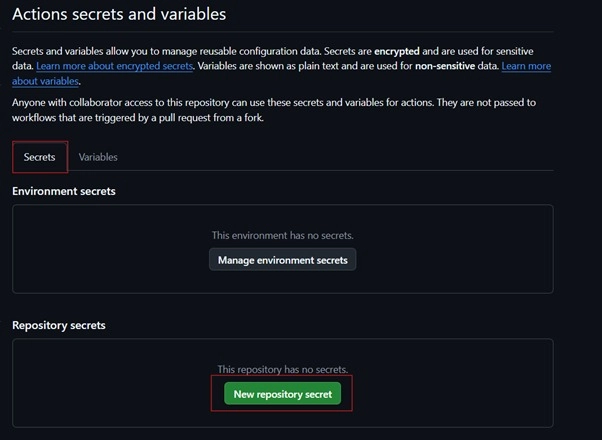
- Enter the secret details:
- Name:
FASTEST_SECRET_KEY(use this exact name) - Value: Paste the token you generated from FASTEST
- Name:
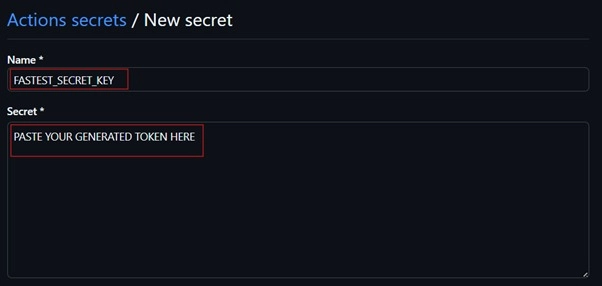
- Click "Add secret" to save
Verification #
After adding the secret:
- The secret will appear in your repository's secrets list
- FASTEST can now authenticate with your repository
- You'll see a confirmation indicator in the FASTEST dashboard
Step 2: Add Workflow Files #
GitHub Actions workflow files automate the integration between GitHub and FASTEST.
Prepare Workflow Directory #
1. Check Directory Structure
- Ensure the
.github/workflows/directory exists in your repository root - If it doesn't exist, create it:
mkdir -p .github/workflows/
2. Directory Structure
your-repository/
├── .github/
│ └── workflows/ ← Workflow files go here
│ ├── fastest-analysis.yml
│ └── fastest-execution.yml
├── src/
├── tests/
└── ...
Copy Workflow Files #
1. Access Workflow Templates
- In your FASTEST configuration tab, you'll find provided workflow files
- These are typically
.ymlfiles specifically designed for FASTEST integration
2. Download and Install
- Copy the provided workflow files into your
.github/workflows/folder - Common workflow files include:
fastest-analysis.yml: Handles code analysis and test case selectionfastest-execution.yml: Manages test execution and result reporting
3. Workflow Configuration
The workflow files typically include:
- Triggers: When the workflow runs (on pull requests, pushes, etc.)
- FASTEST Integration: Steps to communicate with FASTEST platform
- Test Execution: Commands to run selected test cases
- Result Reporting: Send results back to FASTEST
Example Workflow Structure #
name: FASTEST Analysis on: pull_request: branches: [main, master, develop] jobs: fastest-analysis: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: Run FASTEST Analysis env: FASTEST_SECRET_KEY: ${{ secrets.FASTEST_SECRET_KEY }} run: | # FASTEST analysis steps
Step 3: Trigger the Workflow #
Once your secret key and workflow files are configured, you can activate the FASTEST integration.
Workflow Triggers #
The integration can be triggered through several methods:
1. Create New Pull Request #
- Create a new pull request in your repository
- The workflow will automatically trigger when the PR is opened
- FASTEST will analyze changes and generate test recommendations
2. Push to Existing Pull Request #
- Push new commits to an existing pull request branch
- Each push triggers a new analysis cycle
- Updated test recommendations will be generated
3. Manual Workflow Trigger #
- Some workflows can be manually triggered from the GitHub Actions tab
- This is useful for testing the integration setup
Branch Configuration #
Default Branch Analysis #
- By default, FASTEST analyzes changes against your repository's default branch
- Common default branches:
main,master,develop - The workflow compares your pull request changes against this baseline
Custom Base Branch Selection #
If your pull request is based on a different branch:
- Automatic Detection: FASTEST may automatically detect the correct base branch
- Manual Selection: Use the FASTEST interface to manually select the appropriate base branch
- Accurate Comparison: This ensures precise change analysis and relevant test selection
Analysis Results Generation #
Once triggered, FASTEST will:
1. Analyze Code Changes
- Compare current branch with base branch
- Identify modified files and functions
- Assess impact on existing test cases
2. Generate Test Recommendations
- Direct Mapping: Tests directly related to changed code
- Hotspot Analysis: Tests for frequently modified areas
- Historical Failure Prediction: Tests based on historical failure patterns
3. Present Results
- Display recommended test cases in FASTEST dashboard
- Provide analysis insights and reasoning
- Enable test case review and modification
Troubleshooting Integration Issues #
Common Issues and Solutions #
Secret Key Problems #
- Invalid Token: Regenerate token in FASTEST and update GitHub secret
- Wrong Secret Name: Ensure secret is named exactly
FASTEST_SECRET_KEY - Permissions: Verify you have admin access to configure repository secrets
Workflow Issues #
- File Location: Confirm workflow files are in
.github/workflows/directory - File Format: Ensure workflow files are valid YAML format
- Syntax Errors: Check workflow syntax using GitHub's workflow validator
Trigger Problems #
- Branch Protection: Ensure workflows can run on protected branches
- Permissions: Verify GitHub Actions are enabled for your repository
- Token Scope: Confirm FASTEST token has necessary permissions
Integration Verification #
To confirm successful integration:
- Dashboard Status: Check repository status in FASTEST dashboard
- GitHub Actions: Review workflow execution in GitHub Actions tab
- Test Run: Create a test pull request to verify the complete workflow
- Log Review: Check workflow logs for any error messages
Next Steps #
With GitHub integration complete:
- Analysis & Execution: Begin using FASTEST for automated test case selection
- Review Results: Examine analysis results and test recommendations
- Optimize Workflow: Fine-tune settings based on your team's needs
- Monitor Performance: Track testing efficiency improvements
Your repository is now fully integrated with FASTEST and ready for intelligent test optimization!